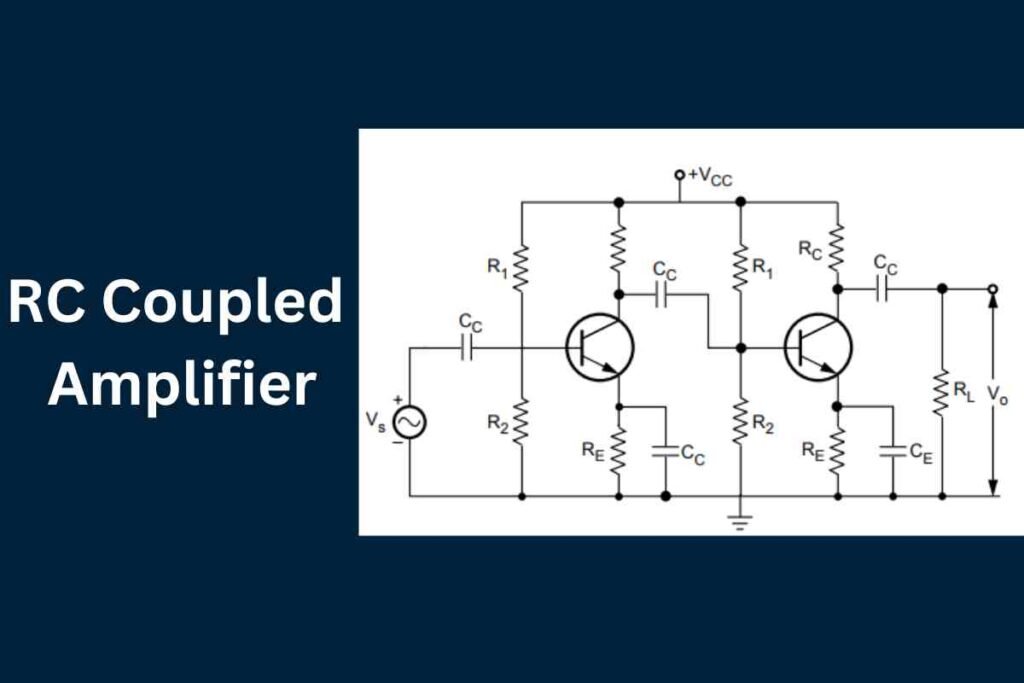
An RC coupled amplifier is a widely used electronic circuit designed for signal amplification. It uses a combination of resistors and capacitors to connect different stages of an amplifier, allowing the transmission of an amplified signal.
In this article, we will explore the core concepts of an RC coupled amplifier, its working principle, advantages, disadvantages, and various applications.
What is an RC Coupled Amplifier?
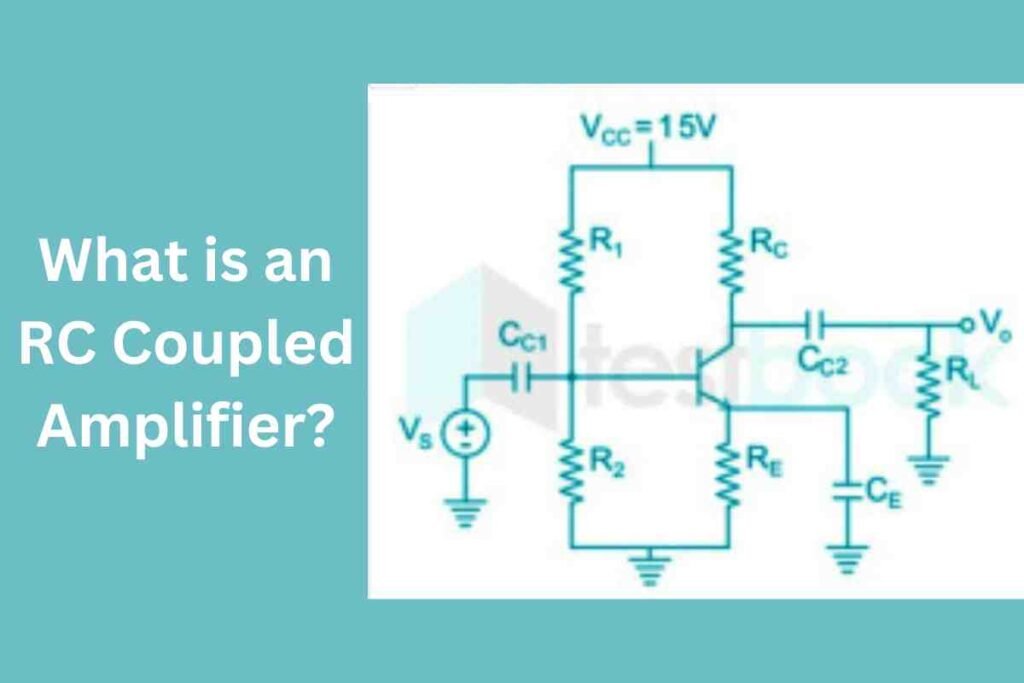
An RC coupled amplifier is a type of multi-stage amplifier in which individual stages are connected using a resistor-capacitor network.
These networks play a crucial role in transferring AC signals between stages while blocking any DC component. This allows each stage to function independently without affecting the biasing conditions of the others.
The key components in an RC coupled-amplifier are:
- Resistor (R): Used for biasing the transistor.
- Capacitor (C): Used for coupling signals between stages.
The circuit usually involves common emitter amplifier stages, where the signal is amplified by each transistor and passed to the next stage through a coupling capacitor.
Working Principle of RC Coupled Amplifier
The working principle of an RC coupled-amplifier is based on using a coupling capacitor to block DC components and allow the AC signal to pass through. Here’s how the process works step-by-step:
- Input Signal: An AC signal is applied to the base of the transistor in the first stage of the amplifier.
- Amplification: The input signal is amplified by the transistor, and the output appears at the collector with a phase shift of 180 degrees.
- Coupling Capacitor: The AC component of the signal is passed through the coupling capacitor, while the DC component is blocked.
- Next Stage: The AC signal enters the next stage of the amplifier and is amplified again.
In a multi-stage amplifier, the output from each stage is further amplified, and this cascading effect increases the overall gain.
However, the gain of the amplifier can slightly decrease due to the loading effect, where each stage’s impedance affects the next.
Frequency Response of RC Coupled Amplifiers

The frequency response of an RC coupled-amplifier refers to how the amplifier behaves across different frequencies. The amplifier exhibits a relatively stable gain in the mid-frequency range but faces issues at both low and high frequencies:
- At Low Frequencies: The coupling capacitor has a high reactance, which reduces the signal passing through. Additionally, the emitter capacitor fails to effectively bypass the emitter resistor, further reducing gain.
- At High Frequencies: The low reactance of the coupling capacitor mimics a short circuit, increasing the loading effect on the next stage. This results in a reduced voltage gain.
- Mid-Frequency Range: In this range, the coupling capacitor’s decreasing reactance typically increases the gain. However, the loading effect compensates for this, keeping the gain relatively constant.
Advantages of RC Coupled Amplifiers
Despite its limitations, the RC coupled-amplifier has several advantages that make it a popular choice in various applications:
- Cost-Effective: Since only resistors and capacitors are used, RC coupled amplifiers are inexpensive and economical.
- Compact Size: The simple design makes it a compact solution for amplifying small signals.
- Stable Gain: The amplifier provides a constant gain over a wide frequency range, making it suitable for mid-frequency applications.
- Easy to Build: The circuit is straightforward and easy to assemble, making it ideal for beginners in electronics.
Disadvantages of RC Coupled Amplifiers
Although RC coupled-amplifiers have numerous benefits, they come with certain drawbacks:
- Unsuitable for Low Frequencies: Due to the behavior of the coupling and emitter capacitors at low frequencies, the amplifier may not perform efficiently at very low frequencies.
- Reduced Gain at High Frequencies: At high frequencies, the increased loading effect can reduce the amplifier’s overall gain.
- Impedance Matching Issues: The output impedance is much higher than the impedance of the device at the end of the circuit, which can be a problem when driving speakers or other load devices in public address systems.
- Moisture Sensitivity: These amplifiers can become noisy over time, particularly in humid environments, affecting performance.
- Narrow Bandwidth: Compared to other amplifiers like JFET amplifiers, RC coupled amplifiers have a narrower bandwidth.
Applications of RC Coupled Amplifiers
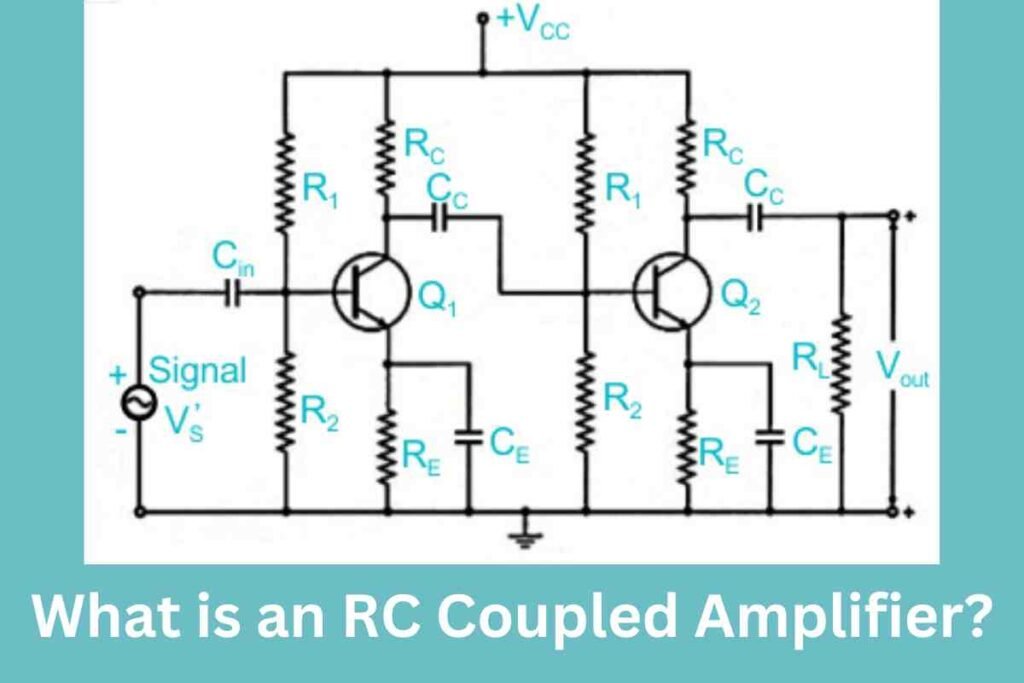
Despite their limitations, RC coupled amplifiers are widely used in various applications, particularly where cost and simplicity are key factors. Here are some common uses:
- Radio Frequency (RF) Communications: RC coupled-amplifiers are used to amplify weak signals in RF circuits, especially in low to medium frequency ranges.
- Public Address Systems: They serve as pre-amplifiers in PA systems to boost microphone signals before transmission.
- Optical Fiber Communications: They are used to amplify signals in fiber-optic communication systems, enhancing signal integrity over long distances.
- Small Signal Amplifiers in Receivers: In radio or television receivers, these amplifiers are used to amplify small signals and improve reception quality.
- Controllers and Sensors: They are integrated into control systems and sensor circuits to amplify signals for processing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the RC coupled amplifier is a reliable and cost-effective solution for amplifying small signals in various applications.
While it offers benefits such as ease of construction, compact size, and stable gain in the mid-frequency range, it is not suitable for high or low-frequency amplification.
By understanding its working principle, advantages, disadvantages, and applications, engineers and designers can decide when to use this amplifier in their circuits.
Whether for RF communications, public address systems, or small signal amplification, the RC coupled amplifier remains an essential tool in electronics.
Looking for more great reads? Check out our homepage maxxfour.in for trending articles and insightful blog posts on various topics.
FAQs
What is the purpose of the coupling capacitor in an RC coupled amplifier?
The coupling capacitor passes AC signals while blocking DC components, ensuring that the DC bias of one stage does not affect the next stage.
What are the key components of an RC coupled amplifier?
The key components include resistors, capacitors, and transistors, which work together to amplify signals.
How does the RC coupled amplifier increase gain?
The amplifier cascades multiple stages, each amplifying the signal, and the overall gain is the product of the individual stage gains.
What is the frequency response of an RC coupled amplifier?
The amplifier has a stable gain in the mid-frequency range, but the gain drops at low and high frequencies due to reactance issues with the coupling and emitter capacitors.
What are the main disadvantages of an RC coupled amplifier?
The main disadvantages include poor low-frequency response, reduced gain at high frequencies, and impedance matching issues.